The Epidermis is the interface between the plant and its environment. Consequently, many adaptations have evolved to foster existence in terrestrial ecosystems. There are four important structures in this image. A= Typical Epidermal cell with wavy walls; B=Guard Cells; C= stalk of secretory Trichome; D=Secretory Cells of the Trichome. |
|||
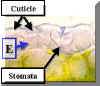
  Agave (Spanish Bayonet) This is a plant which lives in dry (Xeric) ecosystems. Its epidermis contains several important adaptations. |
|||
Sectional view of a
typical |
Agave |
||
Surface view of Agave
epidermis - Epidermal cells can have |
|||
Agave epidermal cells
viewed with polarized light. These cells |
|||
| Lecture
Directory |
Sclerenchyma-1 |
Next Page |
|
|---|---|---|---|