The Vascular Cambium is the source of Secondary Xylem in Dicots. Some Monocots have a Lateral Meristem called the Secondary Thickening Meristem which produces Secondary vascular tissues. We will deal with the Secondary Thickening Meristem later.
Preiclinal divisions in the
Vascular Cambium 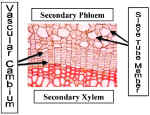 produce radial rows of cells.
Those displaced to the inside become Secondary Xylem. Because the walls of xylem cells are
generally thick and lignified, they resist compression and decay. Secondary xylem that
accumulates substantially over time is called Wood.
produce radial rows of cells.
Those displaced to the inside become Secondary Xylem. Because the walls of xylem cells are
generally thick and lignified, they resist compression and decay. Secondary xylem that
accumulates substantially over time is called Wood.