Link to Placentation 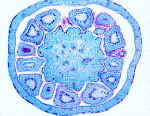 |
The Ovary Wall is called Pericarp (Around the Carpel) and consists of the same old tissues.
The Pericarp has three layers namely,
the Exocarp (Outer Layer of the Carpel),
the Mesocarp (Middle Layer) and
the Endocarp (Inner Layer)
The Exo- and Endocarps are essentially Epidermal tissues, like the adaxial and abaxial surface layers of a vegetative leaf.
The Mesocarp resembles the Mesophyll!
See!!! I told you that Plants are Simple!!!.
Vascular Bundles are present amid the Ground Tissue of the Mesocarp. There are typically 3 bundles in each flower organ. However, fusion and elimination can result in the presence of 1 bundle.
Petals & Stamens may have only one vascular bundle.
Carpels have 3-5 vascular bundles. The largest bundle is called the Dorsal Trace and corresponds to the Midvein of the Leaf. The outermost bundles are called Marginal or Ventral Traces. Intervening Bundles are called Lateral Traces.In some cases there are many large & small Vascular Bundles in each Carpel.
The vascular systems of Perigynous and Epigynous flowers is complicated due to the adnation of flower parts & the Receptacle.