Databases & stats packages
Software must be able to exchange data. For example, point data (e.g.
using latitude-longitude coordinates) compiled in a database should be
convertable into gridcell data for analysis of diversity among areas using
WORLDMAP. Similarly, gridcell scores from WORLDMAP should be exportable
for analysis against non-biological information in statistical packages,
or indeed for display in commercial cartographic packages.
WORLDMAP is based on the same database -
analytical tools - map graphics model as many commercial
geographic information systems (GISs). Three main kinds of data exchange
are supported:
Data import/export
from the database module
Data import
Currently, data can be imported in a range of formats (see the WORLDMAP
Help file for details). These formats include can be exported by several
common databases, such as PARADOX. Other formats can be added by arrangement.
Formats include:
-
comma-delimited text
-
quote- and comma-delimited text (by cell code, or by lat/long)
-
The Nature Conservancy (USA) - example of a tailored long/lat text format
-
DMAP
Data export
Data can be exported in a range of formats (see the WORLDMAP Help file
for details). Other formats can be added by arrangement. Formats include:
-
data matrix
-
comma-delimited text
-
quote- and comma-delimited text
-
Cornell condensed format (read by CANOCO, DECORANA, TWINSPAN)
-
DMAP
Data summary reports
Data can be summarised in a variety of text formats:
-
data matrix
-
list taxa with classification codes
-
list of localities by taxa
-
list of taxa by localities
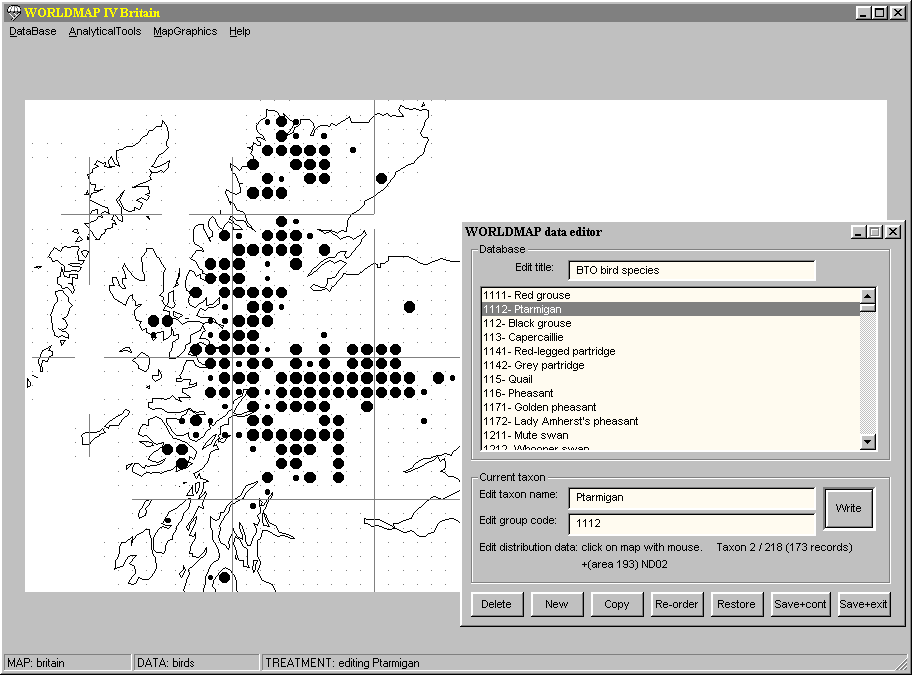
Manual data entry
Data can be entered manually using the point-and-press data editor
(see the WORLDMAP Help file for details):
Screen scores
import/export from the map graphics module
Screen scores import
An ASCII text format allows (see the WORLDMAP Help file for details,
other formats can be added by arrangement):
-
externally generated quantitative measures to be displayed (this has been
used to import quantitative environmental information in order to be overlayed
and compared with internally generated diversity scores)
-
transfer of scores between copies of the program running side by side on
the screen simultaneously
-
scores can be imported by cell number or coordinates.
Screen scores export
The same ASCII text format allows:
-
export of calculated scores for analysis by statistics packages, such as
STATISTICA
-
export of calculated scores for display by cartographic software
-
transfer of scores between copies of the program running side by side on
the screen simultaneously
Image export from
the map graphics module
Maps can be saved as (device-independent) bitmap files (.BMP, see the
WORLDMAP Help file for details). This allows them to be manipulated in
most bitmap graphics packages (such as PaintShopPro) to add features, add
labels, re-colour, crop, save in different formats etc. Such images can
then be inserted into word-processor documents, or into web pages.
Much higher resolution can often be obtained (giving near-vector-quality
images) by using the Print option (see the WORLDMAP Help file for details).
This sends the instructions for drawing the image components direct to
the printer driver software. Consequently the apparent resolution of the
final image is controlled by the printer driver and printer, and their
resolution is often effectively much higher than the screen display that
is used to generate bitmaps.
The Print option can produce encapsulated PostScript images by using
a Print-to-file option with a suitable Windows printer driver. These images
can be edited using vector graphics packages (such as CorelDraw, Adobe
Illustrator) to add features, add labels, re-colour, crop, save in different
formats etc. Such images can then be printed in large format for high resolution
posters etc.



Copyright
(c) 1998 The Natural History Museum. Please read the disclaimer.
