Nutrients are dissolved in water H2O
Properties of Water
1. 90% of Weight of Plant
2. Wonderful Solvent
3. Reactant or Product of Reactions
4. High Specific Heat
5. Evaporative Cooling
Where do plants get their water?
1. Precipitation = Rain, snow, sleet, hail
2. Run-off = Streams, rivers
3. Water table = Ponds, lakes
4. Soil water
5. Aquifers and springs
Horizon A = leached topsoil
Horizon B = accumulated subsoil
Erosion fits in here somewhere!
| Friable! | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mud | --------> | Field Capacity | --------> | Wilting Point | --------> | Dry! |
| | V Gravitational Water (erosion!) | | V Capillary Water (used by plants) | | V Hygroscopic Water (unavailable) |
Clay = high water capacity, high hygroscopic
Sand = low water capacity, low hygroscopic
Irrigation = keeping soil friable!
1. Natural-hope for 4" of rain each month...weather reportHOW MUCH, HOW FREQUENTLY?
2. Sprinkler-washes off mites, insects, dust+kills "eggs" of many "bugs"3. Surface-reduces fungi but raises salts to upper soil
+may apply fertilizer/insecticide at same time
-WASTES WATER
-WATER DROPS ON LEAVES = DEAD SPOTS
-HUMIDITY + = FUNGI +
Moveable vs StationaryFurrow irrigation = between rows in crops4. Trickle Irrigation
Flood irrigation = perimeter furrows, ground level, no runoff-laser guided earth graders-less water/fertilizer/pesticide used5. Wick Irrigation -pots on wet mats (overload) or wicks
-no pulse of these
To keep it friable (between field cap. and wilting point)When in day?
Not like people: 3-squares with 8 glasses
Green Thumb? Dirty Finger!
Meters unreliable!
House Plants:Soak to Field Capacity
let dry to wilting point
soak again, etc.
Early AM so it evaporates before sun hot
NEVER evening, warm but cooling leads to FUNGI
*Too dry? Hydrophobic, water runs off = flash floods
*Friable ideal
*Too wet? Air excluded from space in soil = anaerobic so plants die!
What to do?
Pots with holes
Perlite in mix
Tile fields
Less Frequent but DEEPER irrigation beneficial
Preserve Water by:
Mulch = plastic, stone, paper, leaves, straw (-evap)
Weeding = controlled spacing (-competition)
Terrarium for plant storage for vacations (Plastic bag)
Symptoms of watering trouble:
Excess moisture:Root Death because of no air in soilDeficient moisture:
Fungi Thive (Damping Off of seedlings)
Cracking (Cabbage, Fruits, Roots)
If roots die, plants WILT!Growth inhibition - Abscisic Acid Produced
Brown tips
Abscission of Leaves -Ethylene Produced
Plants WILT!
BROWN FINGERS not GREEN THUMB!
Most people kill by overwatering!
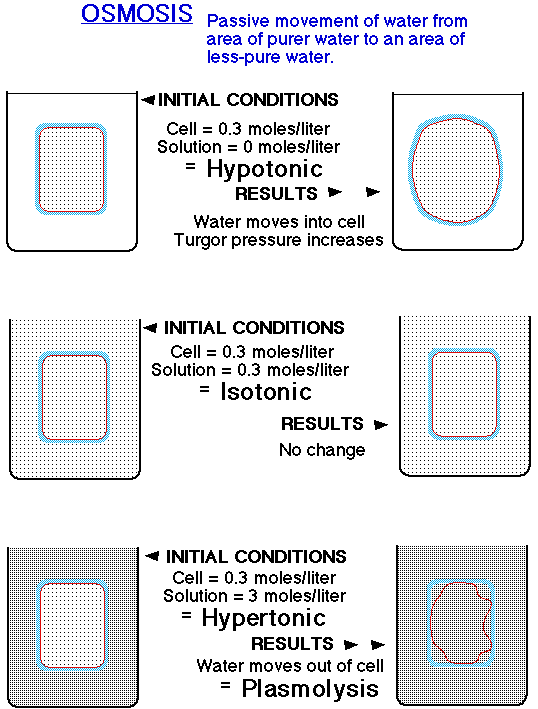
Osmosis explains this:
Movement of Water from purer water toward saltier water

Isotonic = No net change (no growth possible)
Hypertonic = Water leaves, Turgor lost, Wilts
Celery wilted in refrigerator...what to do?
Hydroponics = water culture without soil
nutrients, aeration, support are major problems!
1/10 strength + Perlite
Why water?
1. Photosynthesis (CO2 + H2O --- light ---> CH2O + O2)
2. Prevent Wilting (permit growth)
3. Disolve Minerals in Soil
4. Transpiration - soil>root>stem>leaf>atmosphere in XYLEM
5. Translocation - leaf>stem>flower>fruit>apical bud
leaf>stem>root
in PHLOEM
6. Evaporative Cooling - leaf>atmosphere
Factors Affecting How Much Water is Needed
1. Stage of GrowthSeedling = low but EVEN2. Environment
Reproduction = high
Dormant = lowTemperature: High = more3. Soil
Light: High = more
Humidity: High = less
Wind: High = moreClay = less4. Plant Characteristics
Sand = moreSucculent = less
Waxy = less
Hairy = less
Fine/thin leaves = more
Deep rooted = less
Go back to the Course Schedule.