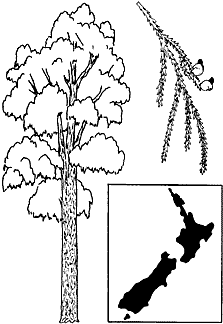
Sketch of rimu, its cone and range (8).
Rimu clearcut in Charleston Forest on 4-Mile Road (7). (This is the best I could do for a rimu photograph -- New Zealand seems to focus on this species mainly for its value as wood).

Distinguishing characteristics include: "cone erect on upturned vegetative shoot, green; bracts narrow, leaf-like, the largest with a single ovule; ovule obliquely inclined towards cone axis, partially inverted; cone 4 mm x 2 mm" [J.H. Johns] (6).

Further distinguishing characteristics: ": seed inclined towards cone axis, ovoid, smooth, slightly plano-convex dorsiventrally, blue-black; micropyle indistinct; epimatium thinly fleshy, thicker below, pink-red; cone bracts swollen, fused, thickly fleshy, pink-red; cone 8 mm x 4 mm." [J.H. Johns] (6).
Common Names
Rimu (1), red pine (2).Taxonomic notes
"In wood anatomy and chemical constituents, D. cupressinum shows such close affinities with species of Podocarpus that it may rightfully belong to that genus" (4).Description
"A tree pyramidal when young, with graceful pendulous branches, but acquiring a round-topped crown when mature, [18-55 m tall] with a trunk [60-150 cm in diameter]. BARK dark brown or grey, shed in large scales. Juvenile foliage loosely arranged, the leaves awl-shaped, [4-6 mm] long, spreading, decurrent, gradually passing into the mature state, the leaves of which are much smaller, [2-3 mm] long, linear, sharp-pointed, or the upper ones often blunt and incurved, keeled on the back. MALE STROBILI small, green, at the tips of branchlets. SEEDS ovoid, slightly compressed, about [3 mm] long, receptacle and bracts occasionally enlarged, fleshy" (4).Range
New Zealand (1). More information on habitat.Big Tree
A tree 42 m tall and 253 cm dbh is recorded from near Pureora, New Zealand (5).Oldest
To 800 years (2).Dendrochronology
The species poses problems because is subject to ring wedging. "Ring wedging occurs when rapid radial growth occurs over several years in certain segments of the tree's circumference, while being extremely slow or absent in others... Examination of complete cross sections can help overcome this problem, and for some species accurate age counts must be based on cross sections rather than increment cores" (2). However, it has been used in at least one climate change study (3).Ethnobotany
It is an important timber tree. The wood is "dark-reddish in colour, with darker or lighter markings, often finely figured; very durable, strong, and a very useful timber for building purposes, bridge construction, railway sleepers, posts, the indoor finish of houses, furniture, and other work. As the wood takes a good polish, finely figured examples are prized for cabinet work. The bark contains a good deal of tannin and is said to impart a reddish colour to leather" (4).Observations
Remarks
See also Paleobotany of Australia and New Zealand conifers.Citations
(1) Silba 1986.(2) Norton & Ogden 1990.
(5) Burstall & Sale 1984.
(6) Molloy 1995.
(7) Native Forest Action. [no date]. Skid Site. URL = http://www.converge.org.nz/nfa/skidsite.htm, accessed 12-Feb-2000.
(8) Anonymous. [no date]. Identification of Trees in Natural Forests. URL = http://www.insights.nzforestry.co.nz/07.htm, accessed 12-Feb-2000.
See also:
M.C. Smale, B.R. Burns, P.N. Smale and P.T. Whaley. 1997. Dynamics of upland
podocarp/broadleaved forest on Mamaku Plateau, central North Island, New
Zealand. Journal of the Royal Society of New Zealand 27: 513-532.
ABSTRACT: Forest composition was examined on one hectare of upland
Dacrydium cupressinum-Prumnopitys taxifolia/Weinmannia racemosa-Beilschmiedia
tawa forest on south Mamaku Plateau, central North Island, New Zealand, a site of
catastrophic volcanic disturbance c. 1900 years ago. ... Tree ferns, mostly
Dicksonia squarrosa and Cyathea smithii, ... dominated basal area in
younger (< 80 yr) forest; D. cupressinum dominated basal area in older (>
80 yr) forest. ... Emergent D. cupressinum and P. taxifolia
sampled were aged between apprx400 and apprx1000 yr; established seedlings of
both species were rare. Much younger Prumnopitys ferruginea
occurred commonly but only up to small tree size; Podocarpus totara
was present only as long-dead fallen trees. Broadleaved species were all much
younger (< apprx250 yr). Shade-tolerant P. ferruginea, ... regenerate
continuously in the understorey of high forest, although P. ferruginea
requires some canopy opening to develop beyond sapling size. ... Larger-scale
studies over longer time periods and over larger areas are needed to determine
definitively the regeneration strategies of the conifers. The unexpectedly high
proportion of building-phase forest suggests a period of substantial canopy
collapse within the past century. Widespread fallen podocarps on the forest
floor indicate the presence of dense conifer forest on the site in the
discernible past, ...
back | Dacrydium | Podocarpaceae | home
This page is from the Gymnosperm Database
URL: http://www.geocities.com/~earlecj/po/da_m/cupressinum.htm
Edited by Christopher J. Earle
E-mail:
earlecj@conifers.org
Last modified on 12-Feb-2000
