Drawing of the largest known grand fir, on the Duckabush River [Robert Van Pelt] (2).
Common Names
Grand, lowland, white, silver, yellow or stinking fir (4), sapin grandissime (6).Taxonomic notes
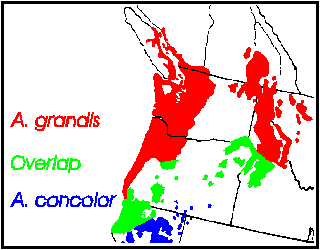
Syn: A. amabilis Murr. not Forbes, A. excelsior Franco, A. gordoniana Carr. (5), Pinus grandis Douglas ex D. Don 1832 (6). " Abies grandis is rather uniform morphologically and chemically. At its southern limit in southern Oregon and northern California, it introgresses with A.concolor (7, 8; Zobel 1973). In the area of introgression, specimens in lower, wetter habitats are best assigned to A. grandis ; those in higher, drier habitats, to A. concolor . Others are best considered to be A.concolor × grandis " (6).Description
Trees to 75 m tall and 155 cm dbh; "crown conic, in age round topped or straggly. Bark gray, thin to thick, with age becoming brown, often with reddish periderm visible in furrows bounded by hard flat ridges. Branches spreading, drooping; twigs mostly opposite, light brown, pubescent. Buds exposed, purple, green, or brown, globose, small to moderately large, resinous, apex round; basal scales short, broad, equilaterally triangular, slightly pubescent or glabrous, resinous, margins entire, apex pointed or slightly rounded. Leaves (1)2-6 cm × l.5-2.5 mm, 2-ranked, flexible, with leaves at center of branch segment longer than those near ends, or with distinct long and short leaves intermixed, proximal portion ± straight, leaves higher in tree spiraled and 1-ranked; cross section flat, grooved adaxially; odor pungent, faintly turpentinelike; abaxial surface with 5-7 stomatal rows on each side of midrib; adaxial surface light to dark lustrous green, lacking stomates or with a few stomates toward leaf apex; apex distinctly notched (rarely rounded); resin canals small, near margins and abaxial epidermal layer. Pollen cones at pollination bluish red, purple, orange, yellow, or ± green. Seed cones cylindric, (5)6-7(12) × 3-3.5 cm, light green, dark blue, deep purple, or gray, sessile, apex rounded; scales ca. 2-2.5 × 2-2.5 cm, densely pubescent; bracts included. Seeds 6-8 × 3-4 mm, body tan; wing about 1.5 times as long as body, tan with rosy tinge; cotyledons (4)5-6(7). 2 n =24" (6).
Range
Canada: British Columbia; USA: Montana, Idaho, Washington, Oregon and California at 0-1500 m in moist conifer forests (6). See also (11).Big Tree
Largest volume: Height 77 m, dbh 185 cm, stem volume 68.3 m 3 in 1988; along Duckabush River Trail, Olympic National Park, WA (2).Largest diameter: Height 75.0 m, dbh 220 cm; along the Chilliwack River, BC (9).
Tallest: Height 81.4 m, dbh 158 cm, stem volume 53.0 m 3 in 1993; in the Glacier Peak Wilderness, WA (2).
Oldest
Without supporting data, ages of over 300 years have been claimed (10).Dendrochronology
Ethnobotany
Observations
Remarks
Citations
(1) Silba 1986 .(2) Van Pelt 1996 .
(3) Fowells 1965 .
(4) Peattie 1950 .
(5) Vidakovic 1991 .
(6) Richard S. Hunt at the Flora of North America web site .
(7) Zavarin et al. 1975 .
(8) Hamrick & Libby 1972 .
(9) E-mail communication from Robert Van Pelt, who measured these trees; 18-Mar-1998.
(10) Burns & Honkala 1990 , p. 56.
(11) Robert S. Thompson, Katherine H. Anderson and Patrick J. Bartlein. 1999. Atlas of Relations Between Climatic Parameters and Distributions of Important Trees and Shrubs in North America. U.S. Geological Survey Professional Paper 1650 A&B. URL= http://greenwood.cr.usgs.gov/pub/ppapers/p1650-a/pages/conifers.html , accessed 22-Jan-2000.
See also:
FEIS database
.
Lanner 1983
.
Pojar and Mackinnon 1995
.
[ Abies ] [ Pinaceae ] [ home ]
This page is from the Gymnosperm Database
URL: http://www.geocities.com/~earlecj/pi/ab/grandis.htm
Edited by Christopher J. Earle
E-mail:
earlecj@earthlink.com
Last modified on 22-Jan-2000